What is OLED? How should we choose?
Published:2023-12-14Views:1383
OLED displays have grown in popularity over the past decade, appearing in televisions, portable gaming consoles and smartphones from some of the tech industry's biggest brands. We'll explain what an OLED display is, why it's so popular, why it's better than other displays, and the drawbacks you should know about.

What is OLED?
OLED is the abbreviation of (Organic Light-Emitting Diode), and its Chinese name is organic light-emitting diode. It is a current-type organic light-emitting device that emits light through the injection and recombination of carriers. The luminous intensity is proportional to the injected current.
Under the action of the electric field in OLED, the holes generated by the anode and the electrons generated by the cathode will move, inject into the hole transport layer and electron transport layer respectively, and migrate to the light-emitting layer. When the two meet in the light-emitting layer, they generate energy excitons, which excite the light-emitting molecules and ultimately produce visible light. The basic structure of OLED is a sandwich structure with an organic light-emitting layer (EL, Emission Layer) between the cathode (Cathode) and the anode (Anode).
In short, it is a light source used in a wider range of electronic products, and OLED is widely used in digital signage, TVs, mobile phones and other fields.

Where can OLED displays be used?
1. Commercial field: Small-sized OLED screens can be installed in POS machines, copiers, and ATM machines. Because OLED screens are flexible, thin, light, and have strong anti-aging properties, they are both beautiful and practical. The large screen can be used as a business promotion screen, or as an advertising screen in stations, airports, etc. This is because OLED screens have wide viewing angles, high brightness, bright colors, and the visual effect is much better than LCD screens.
2. Electronic product field: OLED is most widely used in smartphones, followed by notebooks, display screens, TVs, tablets, digital cameras and other fields. Because OLED displays are more colorful and can be adjusted (different display modes) , so it is very widely used in practical applications.
3. Transportation field: OLED is mainly used in ships, aircraft instruments, GPS, video phones, car displays, etc., and is mainly small in size. These fields mainly focus on the wide viewing angle performance of OLED, which can be seen clearly even without looking directly. to the screen content.
4. Exhibition display: OLED transparent display screen is used in corporate exhibitions, exhibition halls, museums and other fields to deeply explore the background and meaning of exhibition display objects, and realize a dynamic display form of vertical depth dissection and horizontal related expansion that is difficult to achieve with ordinary display means. Promote the cooperation of the audience's visual, auditory and other senses and behaviors.

What advanced technologies are used in OLED screens?
Self-illuminating technology: OLED screens use self-illuminating technology, and each pixel can be controlled independently, so it can achieve higher contrast and deeper blacks.
High color saturation: OLED screens have higher color saturation and can display more vivid colors, providing users with a better visual experience.
Wide viewing angle technology: The OLED screen's wide viewing angle technology allows users to view the screen from different angles without color distortion or brightness reduction.
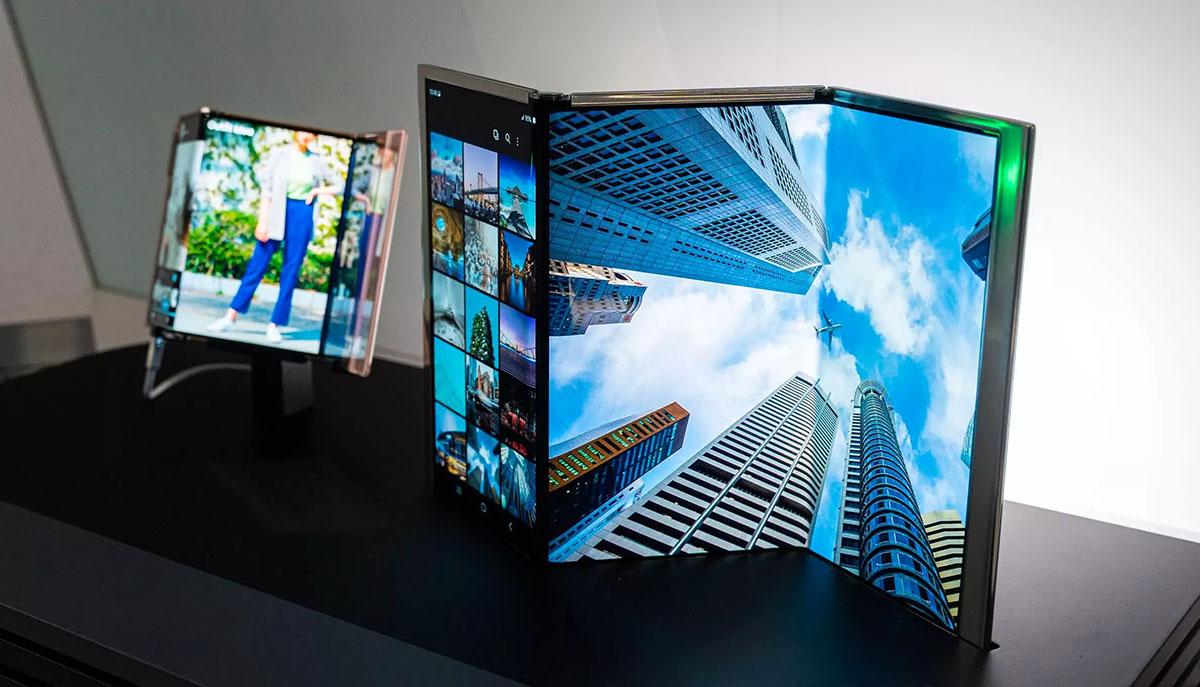
Flexible display technology: OLED screens use flexible display technology and can be made into screens of various shapes and sizes, providing more possibilities for product design. OLED is more flexible than LCD or LED, which expands its uses. You can get curved and rollable OLED displays, like the LG OLED R rollable TV; and as foldable phones and tablets become more popular, you'll see flexible displays in mobile devices like the Microsoft Surface Duo and Samsung Galaxy Z Fold3, they both use flexible AMOLED (active matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays.
Low-power technology: OLED screens have relatively low power consumption, which can extend the battery life of the device.
Energy consumption is also less since no backlight is required to generate light. This makes them a good choice for small devices, as they last a bit longer than their LCD-based counterparts. However, higher-resolution OLED screens reduce battery life because the extra pixel count drains the battery.
What are the disadvantages of OLED?
Screen Brightness: In the world of TVs, OLED isn't as consistently bright as LCD. The relative lack of brightness means LCD LED TVs produce punchier, brighter, more vibrant HDR performance. That said, new technologies like LG Display’s microlens array panels can produce up to 1,700 nits of brightness.

QD-OLED can also achieve higher peak brightness levels, better viewing angles, more accurate colors and better HDR performance. Currently, only Samsung and Sony have launched QD-OLED TVs.
Lifespan Issue: OLED displays don’t last as long as other displays. Because OLED uses organic materials, it degrades over time, causing image performance to deteriorate (color balance changes over time). There is no need to worry about this in the short term as it will take many, many years to happen.
Exorbitant costs: Although costs have come down, OLEDs are more expensive to produce. However, while manufacturing is not cheap, it is still a relatively expensive process. Depending on your market, you can buy an OLED TV for less than £1,000 and a phone for less than £199 - a far cry from just a few years ago.
Insufficient contrast in bright light: OLED works best in low-light conditions because bright light shining directly on the screen affects its contrast. Samsung's Super AMOLED has made advances in this area by deflecting sunlight to make the screen easier to read, while increased brightness helps reduce this effect.
Is it a good time to buy an OLED display?
In our opinion, the advantages of OLED outweigh the disadvantages. It is constantly improving while becoming more affordable. Contrast and black level performance are better than any other display, whether traditional OLED or QD-OLED, resulting in a richer, more impactful performance.
While OLED is still an expensive option, people no longer have to worry about OLED compared to a few years ago. Still, OLED delivers some of the best images.






















































.png)